Automated Re‑Prompting Pipeline
The Automated Re‑Prompting Pipeline improves Large Language Model (LLM) outputs by using AIMon’s Instruction Following Evaluation (IFE) model to detect issues and provide feedback, which the pipeline turns into targeted re‑prompts that guide models toward better responses.
Why it matters:
- Achieve or surpass GPT-4o-level instruction adherence with smaller (3-24B) models
- Boost instruction adherence by ~22% while reducing hallucinations and toxicity
- Integrate seamlessly with any LLM (OpenAI, Together, Anthropic, HuggingFace, etc.)
- Maintain speed and scalability with a fully stateless design
Deep Dive:
Read our Agentic Reflection Part 3: A Smarter Loop for Smarter Models for design decisions, details, and performance insights.
How It Works
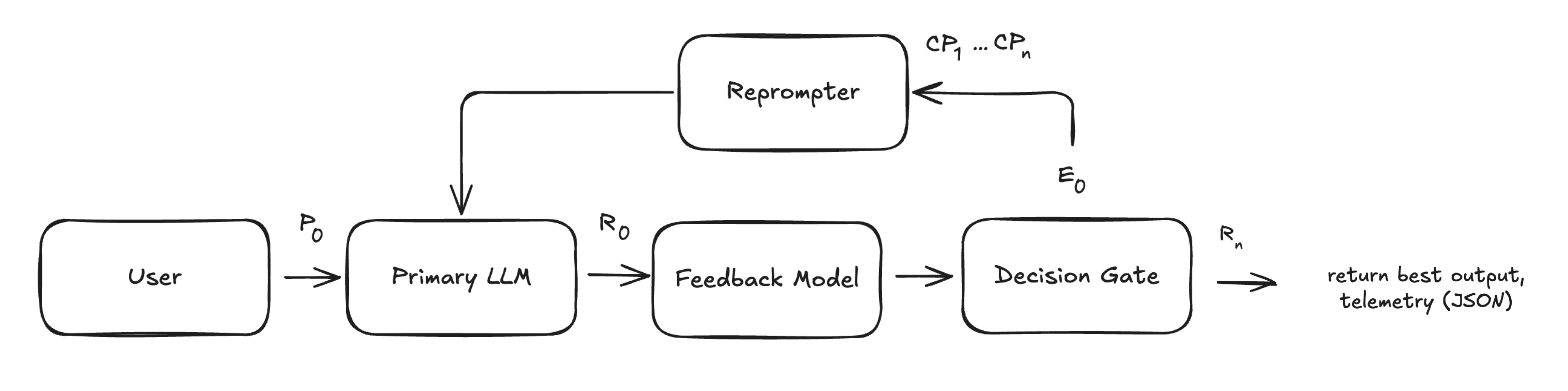
- Generate: Your prompt goes to the primary LLM, which produces an initial response
- Detect: AIMon’s IFE model evaluates the response for instruction adherence, hallucination, and toxicity. It returns a structured report highlighting any violations and explanations.
- Re‑prompt: If issues are detected, the pipeline generates a targeted corrective prompt.
- Refine: The LLM revises its answer using this feedback, repeating until all instructions are adhered to or specified limits (latency or iteration cap) are reached.
Each iteration can log detailed telemetry (JSON), giving you full visibility into how the model improved.
Implementation
Quick Start:
Explore the Re‑Prompting Pipeline Colab Notebook for a step‑by‑step implementation.
run_reprompting_pipeline Function Signature
from aimon.reprompting_api.runner import run_reprompting_pipeline
def run_reprompting_pipeline(
llm_fn: Callable[[str.Template, str, str, str], str],
user_query: str,
system_prompt: str = None,
context:str = None,
user_instructions: List[str] = None,
reprompting_config: RepromptingConfig = None,
) -> dict
Parameters
llm_fn(Callable): Your LLM function.- Takes:
recommended_prompt_template(str.Template): The pipeline-provided template.system_prompt(str): System-level role or behavior definition.context(str): Background context for the model to reference.user_query(str): The main query or task.
- Returns: A string containing the model’s response.
- Takes:
user_query(str): The question or task for the model.system_prompt(str, optional): A high‑level role or behavior definition for the model.context(str, optional): Relevant background text for the model to reference (e.g., a document, policy, or knowledge base excerpt).user_instructions(List[str], optional): Specific, deterministic guidelines for the response. These are what AIMon uses to evaluate and iteratively improve the model’s output.reprompting_config(RepromptingConfig, optional): Controls pipeline behavior such as return values, iteration count, and latency budget.
Returns
dict: A dictionary containing:
best_response(str): The final, improved LLM answer after re‑prompting.summary(str, optional): A short caption summarizing the loop (e.g., "[2 iterations, 0 failed instructions remaining]").telemetry(List[dict], optional): Detailed per‑iteration logs. Each entry includes:iteration(int): The iteration number.cumulative_latency_ms(float): Total elapsed time up to this iteration (in milliseconds).groundedness_score(float): Confidence that the response stays grounded in the provided context (0‑1).instruction_adherence_score(float): Adherence to the provided instructions (0‑1).toxicity_score(float): Detected toxicity level in the response (0‑1). Lower score is better.response_feedback(list): Detailed feedback entries from the IFE model (violated instructions and explanations).residual_error_score(float): Error score between 0 (best) and 1 (worst). Calculated by averaging penalties for each failed instruction and groundedness check and assigning a higher penalty for more severe instruction failures.failed_instructions_count(int): Number of instructions violated in this iteration.stop_reason(str): Why this iteration ended or reason for continuation.- Possible values:
all_instructions_adhered,max_iterations_reached,latency_limit_exceeded,unknown_error,reprompting_failed,instructions_failed_continue_reprompting,toxicity_detected_continue_reprompting
- Possible values:
prompt(str): The corrective prompt template with placeholders sent to the LLM for this iteration.response_text(str): The raw response produced by the LLM.
llm_fn Implementation
To use the re‑prompting pipeline, you must provide your own Callable LLM function. This function acts as the connector between the pipeline and any black‑box model (e.g., TogetherAI, OpenAI, Anthropic, or a local model). The function should take in the following parameters:
recommended_prompt_template(string.Template): the corrective prompt template generated by the pipeline.system_prompt(str): system-level instructions or guidelines for model behavior.context(str): the contextual information or reference material relevant to the query. This is typically passed from a retrieval step or knowledge base.user_query(str): the user question or task.
Return value: Your function must return a single string containing the model's generated response.
Implement your LLM function to do the following:
- Receive the corrective prompt as a string.Template.
- Substitute placeholders (system_prompt, context, user_query) into the template. You can alternatively implement your own template or modify the provided one for more control.
- Send the filled prompt to your chosen model (e.g., TogetherAI, OpenAI, Anthropic, local model).
- Return the model’s response as plain text.
Example Implementation:
The following implementation leverages Gemma4B via TogetherAI, but you can swap model for any Together-hosted model (e.g., 'mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2'). You can also replace the whole block with any LLM call (OpenAI, Claude, HuggingFace, etc.)
Tip: Use
safe_substitute()instead ofsubstitute()to prevent runtime errors if any placeholder values are missing.
from string import Template
from together import Together
TOGETHER_API_KEY = os.environ.get("TOGETHER_API_KEY")
client = Together(api_key=TOGETHER_API_KEY)
def my_llm(recommended_prompt_template: Template, system_prompt, context, user_query) -> str:
# safely substitute placeholders in the pipeline-provided template with appropriate values
filled_prompt = recommended_prompt_template.safe_substitute(
system_prompt=system_prompt,
context=context,
user_query=user_query
)
# replace this block with any LLM call you want. (OpenAI, Claude, HuggingFace, etc.)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="google/gemma-3n-E4B-it",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": filled_prompt}],
max_tokens=256,
temperature=0
)
# extract and return a string output
output = response.choices[0].message.content
return output
RepromptingConfig
The RepromptingConfig object controls how the re‑prompting pipeline behaves.
If no configuration is provided, the pipeline uses the defaults below.
Tip: Enable
return_telemetry=Trueto log every iteration with latency, feedback, and more (see return values above for a breakdown of components logged in telemetry)
Parameters
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
aimon_api_key | str | env:AIMON_API_KEY | API key to call AIMon’s IFE feedback model. |
publish | bool | False | Whether to publish the results to app.aimon.ai. |
max_iterations | int | 2 | Max number of LLM calls (1 initial + reprompts). 2–3 recommended for most use cases. |
return_telemetry | bool | False | Return a JSON blob with per‑iteration metadata (responses, errors, latency). |
return_aimon_summary | bool | False | Return a short summary caption (e.g., "2 iterations, 0 failed instructions"). |
latency_limit_ms | int | None | Abort loop and return the best response if total latency exceeds this value (in ms). |
model_name | str | Random string (aimon-react-model-*) | Model name for telemetry tracking. |
application_name | str | Random string (aimon-react-application-*) | Application name for telemetry tracking. |
user_model_max_retries | int | 1 | Number of exponential backoff retries if llm_fn fails. |
feedback_model_max_retries | int | 1 | Number of exponential backoff retries if AIMon Detect fails. |
Note: If no
aimon_api_keyis passed directly, it must be set in the environment asAIMON_API_KEYfor the pipeline to run.
Error Handling:
Ifllm_fnor the feedback model (IFE) fails after the configured retries, the pipeline raises aRuntimeError. Useuser_model_max_retriesandfeedback_model_max_retriesinRepromptingConfigto adjust retry behavior.
Usage Example
Sample Implementation
from aimon.reprompting_api.config import RepromptingConfig
from aimon.reprompting_api.runner import run_reprompting_pipeline
from string import Template
import json
# load API keys
TOGETHER_API_KEY = os.environ.get("TOGETHER_API_KEY")
AIMON_API_KEY = os.environ.get("AIMON_API_KEY")
# create your llm_fn
client = Together(api_key=TOGETHER_API_KEY)
def my_llm(recommended_prompt_template: Template, system_prompt=None, context=None, user_query=None) -> str:
"""
Example LLM function that:
1. Receives a corrective prompt template (string.Template).
2. Substitutes placeholders (system_prompt, context, user_query).
3. Sends to a Together-hosted LLM and returns the response.
"""
filled_prompt = recommended_prompt_template.substitute(
system_prompt=system_prompt,
context=context,
user_query=user_query
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": filled_prompt}],
max_tokens=256,
temperature=0
)
output = response.choices[0].message.content
return output
# set up your RepromptingConfig
config = RepromptingConfig(
aimon_api_key=AIMON_API_KEY,
publish=True,
return_telemetry=True,
return_aimon_summary=True,
application_name="api_test",
max_iterations=3
)
# set up your input values
user_query = ""
context = ""
system_prompt = ""
user_instructions = []
# run pipeline
result = run_reprompting_pipeline(
llm_fn=my_llm,
user_query=user_query,
system_prompt= system_prompt,
context=context,
user_instructions=user_instructions,
reprompting_config=config
)
# Print outputs
print("\n=== SUMMARY ===")
print(result.get("summary"))
print("\n=== BEST RESPONSE ===")
print(result["best_response"])
print("\n=== TELEMETRY ===")
print(json.dumps(result.get("telemetry"), indent=2))
Integrating with RAG frameworks
The pipeline is retrieval‑framework agnostic, meaning you can integrate it with any RAG system (e.g., LlamaIndex, LangChain, custom retrievers) while maintaining full control over retrieval behavior.
How it works:
- Use your RAG framework to fetch relevant context.
- Normalize the retrieved content into a string (e.g., join text chunks).
- Pass this string into the pipeline using the context parameter.
Limitations
- Requires clear, deterministic instructions. Vague or conflicting ones cannot be fixed
- Subjective attributes (e.g., tone, creativity) improve inconsistently
- Adds latency and cost per iteration (tune
latency_limit_msandmax_iterationsto balance speed with response quality)
Resources and Further Reading
- Agentic Reflection Part 3: A Smarter Loop for Smarter Models: Blog with detailed results and design decisions
- Open‑source Pipeline: Experiment with and extend the pipeline
- Re‑Prompting Pipeline Colab Notebook: Step‑by‑step demo